What is fiber optics?
Fiber optics, the science of transmitting data, voice and images through light through thin, transparent optical fibers. In the field of telecommunications, fiber optic technology has practically replaced copper wires in long distance telephone lines, which are used to connect computers in local area networks. Fiber optics is also the basis for fiber optic endoscopes used to examine the inside of the body (endoscopy) or to examine the inside of manufactured structural products.
What are the optical fibers used in fiber optics made of?
The basic medium for fiber optics is a hair-thin fiber, sometimes made of plastic, but most commonly glass. A typical glass fiber has a diameter of 125 micrometers (μm) or 0.125 mm (0.005 in.). This is actually the diameter of the cladding or outer reflective layer. The diameter of the core or internal transmission barrel can be as small as 10 μm. By a process called total internal reflection, light incident on an optical fiber can travel very long distances within the core with very little attenuation and reduced intensity. The degree of attenuation over distance varies depending on the wavelength of the light and the composition of the fiber.
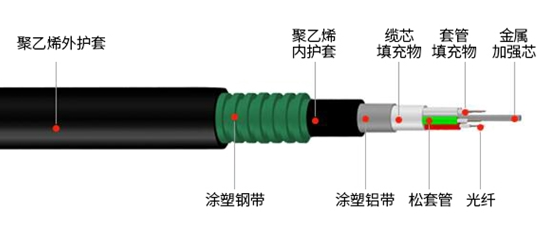
What are the uses of optical fibers?
When glass fibers of the core/cladding design were introduced in the early 1950s, the presence of impurities limited their use to lengths sufficient for endoscopy. in 1966, Charles Kao and George Hockham, electrical engineers working in England, suggested the use of optical fibers for telecommunications, and within two decades, silica glass fibers were produced pure enough that infrared light signals could travel through them for 100 kilometers (60 miles) or more without having to be reinforced by a repeater. in 2009, Kao was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work. Plastic fibers, usually made of polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene or polycarbonate, are cheaper to produce and more flexible than glass fibers, but their greater light attenuation limits their use to shorter connections in buildings or cars.
What type of light is used in optical fiber?
Optical communications are typically performed using infrared light in the wavelength range of 0.8-0.9 μm or 1.3-1.6 μm, which are efficiently produced by light-emitting diodes or semiconductor lasers and have minimal attenuation in glass fibers. Endoscopy or fiber endoscopic inspection in industry is performed at visible wavelengths, where one bundle of fibers is used to illuminate the inspection area with light and another bundle of fibers is used as a slender lens to transmit the image to the human eye or camera.
Why is fiber optics the best method for transmitting data over long distances?
Through the principle of total internal reflection, light incident on an optical fiber can travel great distances within the core with exceptionally clean attenuation or intensity reduction, making optical fiber the ideal method for transmitting data over long distances.
What is fiber optics?
Fiber optics, the science of transmitting data, voice and images through light through thin, transparent optical fibers. In the field of telecommunications, fiber optic technology has practically replaced copper wires in long distance telephone lines, which are used to connect computers in local area networks. Fiber optics is also the basis for fiber optic endoscopes used to examine the inside of the body (endoscopy) or to examine the inside of manufactured structural products.
What are the optical fibers used in fiber optics made of?
The basic medium for fiber optics is a hair-thin fiber, sometimes made of plastic, but most commonly glass. A typical glass fiber has a diameter of 125 micrometers (μm) or 0.125 mm (0.005 in.). This is actually the diameter of the cladding or outer reflective layer. The diameter of the core or internal transmission barrel can be as small as 10 μm. By a process called total internal reflection, light incident on an optical fiber can travel very long distances within the core with very little attenuation and reduced intensity. The degree of attenuation over distance varies depending on the wavelength of the light and the composition of the fiber.

What are the uses of optical fibers?
When glass fibers of the core/cladding design were introduced in the early 1950s, the presence of impurities limited their use to lengths sufficient for endoscopy. in 1966, Charles Kao and George Hockham, electrical engineers working in England, suggested the use of optical fibers for telecommunications, and within two decades, silica glass fibers were produced pure enough that infrared light signals could travel through them for 100 kilometers (60 miles) or more without having to be reinforced by a repeater. in 2009, Kao was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work. Plastic fibers, usually made of polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene or polycarbonate, are cheaper to produce and more flexible than glass fibers, but their greater light attenuation limits their use to shorter connections in buildings or cars.
What type of light is used in optical fiber?
Optical communications are typically performed using infrared light in the wavelength range of 0.8-0.9 μm or 1.3-1.6 μm, which are efficiently produced by light-emitting diodes or semiconductor lasers and have minimal attenuation in glass fibers. Endoscopy or fiber endoscopic inspection in industry is performed at visible wavelengths, where one bundle of fibers is used to illuminate the inspection area with light and another bundle of fibers is used as a slender lens to transmit the image to the human eye or camera.
Why is fiber optics the best method for transmitting data over long distances?
Through the principle of total internal reflection, light incident on an optical fiber can travel great distances within the core with exceptionally clean attenuation or intensity reduction, making optical fiber the ideal method for transmitting data over long distances.