800G/400G high-speed optical modules, test solutions for different equipment combinations
With the rapid development of the Internet, data centres and cloud computing have an increasingly high demand for network bandwidth. High-speed optical modules, as the core equipment for network transmission, have a direct impact on the performance and quality of network stability and efficiency. At present, 800G and 400G high-speed optical modules have become the mainstream choice for data centres and cloud computing, but how to effectively test these high-speed optical modules to ensure that they meet the relevant technical standards and application requirements is an urgent problem.
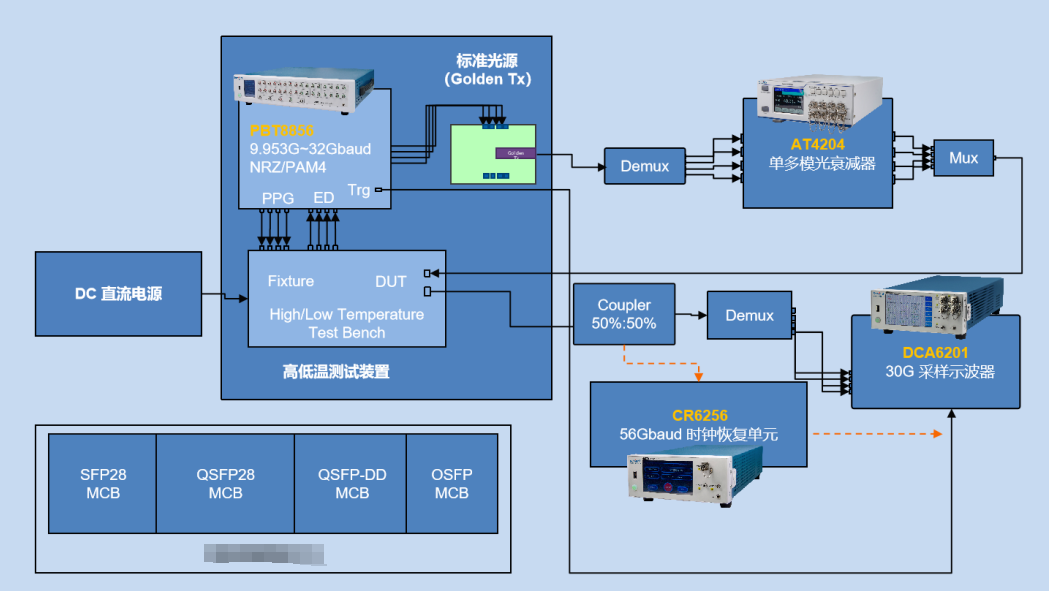
800G/400G high-speed optical module test solution:
- Test environment: The test environment should simulate the actual network environment, including factors such as temperature, humidity, voltage, fibre length, fibre type, fibre connectors, and possible interference and noise. The test environment should be kept stable and consistent to avoid errors and changes in the test results.
- Test equipment: The test equipment should be selected from professional high-speed optical module testers, such as MT8000A from [Anritsu Communications] or DPO70000SX from [Tektronix], etc. These testers can provide high-precision measurements and analyses of parameters such as optical power, optical wavelength, optical frequency, spectra, eye diagrams, BER, etc., as well as the programming and control functions of high-speed optical modules . The test equipment should match the interface and protocol of the test object, such as QSFP-DD, OSFP, CFP8, etc., to ensure the effectiveness and accuracy of the test.
- Test content: The test content should cover all aspects of the high-speed optical module, including optical characteristics, electrical characteristics, functional characteristics, compatibility characteristics, etc., as well as comparison and evaluation with relevant technical standards and application requirements. Specific test content includes:
- Optical characteristics: optical characteristics mainly include optical power, optical wavelength, optical frequency, spectrum, eye diagram, BER and other parameters, which reflect the quality and performance of the optical signal of the high-speed optical module, as well as the degree of matching with the receiving end. When testing the optical characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as PAM4 for 800Gbps or NRZ for 400Gbps, should be considered. When testing the optical characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the optical characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.
- Electrical characteristics: The electrical characteristics mainly include parameters such as voltage, current, power consumption, jitter, and crosstalk, which reflect the quality and performance of the electrical signals of the high-speed optical module, as well as the degree of matching with the host board. When testing the electrical characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, humidity, voltages, fiber lengths, fiber types, fiber connectors and other factors should be considered, as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as 800Gbps PAM4 or 400Gbps NRZ. When testing the electrical characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the electrical characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.
- Functional characteristics: Functional characteristics mainly include the programming and control functions of the high-speed optical module, such as I2C, MDIO, CMIS, etc., which reflect the configurability and manageability of the high-speed optical module, as well as the communication capability with the host board. When testing the functional characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as PAM4 at 800 Gbps or NRZ at 400 Gbps, should be considered. When testing the functional characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the functional characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.
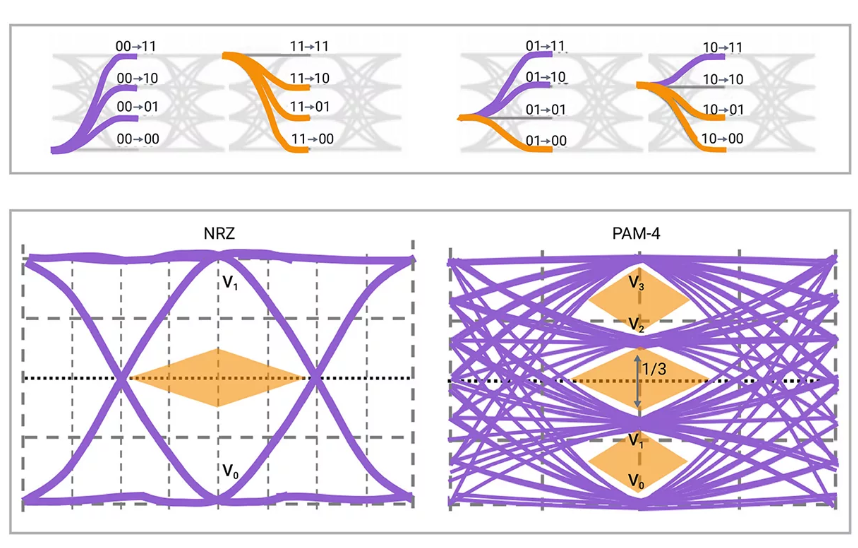
- Compatibility features: Compatibility features mainly include the compatibility of high-speed optical modules with different host boards, switches, routers and other equipment, as well as with different protocols and standards, such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, InfiniBand and so on. When testing the compatibility characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as 800Gbps PAM4 or 400Gbps NRZ, etc., should be considered. When testing the compatibility characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the compatibility characteristics of the high-speed optical modules satisfy the specifications and requirements.
- Test results: Test results should be presented in a clear and objective manner, including data, charts, analyses, evaluations, etc., as well as comparisons and assessments with relevant technical standards and application requirements. The test results should be able to reflect the advantages and shortcomings of high-speed optical modules, as well as possible problems and suggestions for improvement.
800G/400G high-speed optical modules need to use what test equipment?
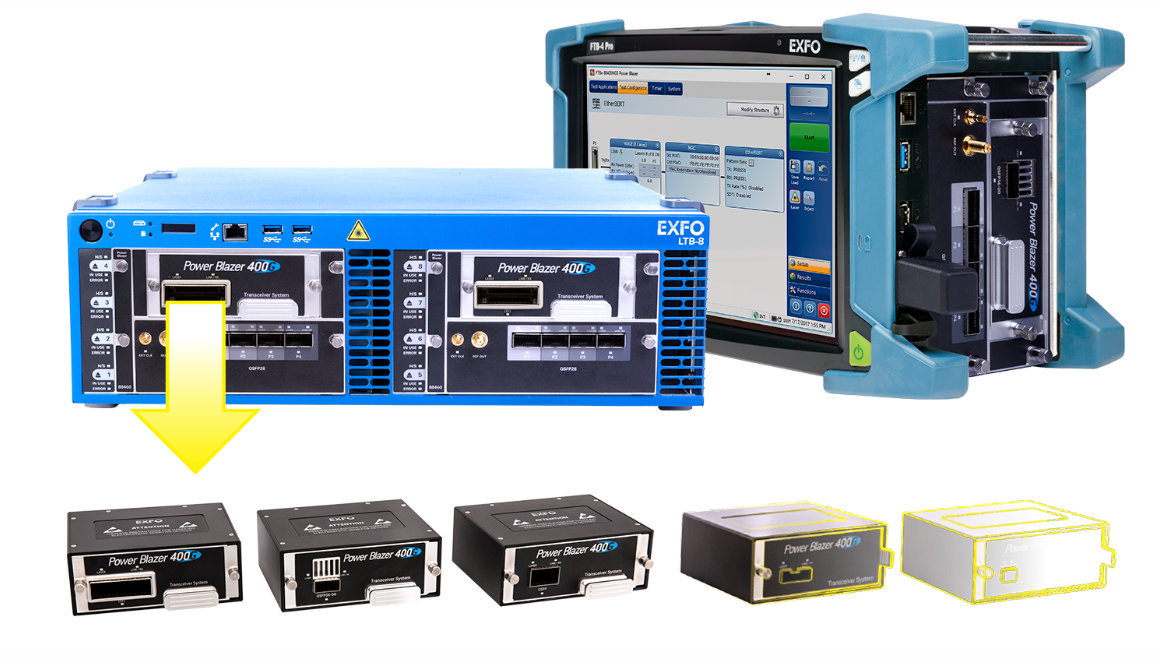
- BER instrument: Used to test the optical module's BER, eye diagram, clock recovery, forward error correction and other parameters, such as the 8-channel 400G PAM4 BER instrument from Unicom Instruments.
- Sampling Oscilloscope: Used to test the optical signal waveform, amplitude, phase, frequency and other parameters of the optical module, such as EXFO's EA-4000 Eye Analyzer.
- Optical Power Meter: Used to test the optical power, spectrum, wavelength and other parameters of optical modules, such as EXFO's FTBx-9160 NEMS optical switch.
- Optical Attenuator: Used to test the sensitivity, dynamic range, signal-to-noise ratio and other parameters of optical modules, such as EXFO's MXS-9100 MEMS Matrix Optical Switch.
- Optical Module Test Board (MCB): Used to connect optical modules and test equipment for serial communication and control, such as EXFO's Module Compliance Boardhtt

With the rapid development of the Internet, data centres and cloud computing have an increasingly high demand for network bandwidth. High-speed optical modules, as the core equipment for network transmission, have a direct impact on the performance and quality of network stability and efficiency. At present, 800G and 400G high-speed optical modules have become the mainstream choice for data centres and cloud computing, but how to effectively test these high-speed optical modules to ensure that they meet the relevant technical standards and application requirements is an urgent problem.

800G/400G high-speed optical module test solution:
- Test environment: The test environment should simulate the actual network environment, including factors such as temperature, humidity, voltage, fibre length, fibre type, fibre connectors, and possible interference and noise. The test environment should be kept stable and consistent to avoid errors and changes in the test results.
- Test equipment: The test equipment should be selected from professional high-speed optical module testers, such as MT8000A from [Anritsu Communications] or DPO70000SX from [Tektronix], etc. These testers can provide high-precision measurements and analyses of parameters such as optical power, optical wavelength, optical frequency, spectra, eye diagrams, BER, etc., as well as the programming and control functions of high-speed optical modules . The test equipment should match the interface and protocol of the test object, such as QSFP-DD, OSFP, CFP8, etc., to ensure the effectiveness and accuracy of the test.
- Test content: The test content should cover all aspects of the high-speed optical module, including optical characteristics, electrical characteristics, functional characteristics, compatibility characteristics, etc., as well as comparison and evaluation with relevant technical standards and application requirements. Specific test content includes:
- Optical characteristics: optical characteristics mainly include optical power, optical wavelength, optical frequency, spectrum, eye diagram, BER and other parameters, which reflect the quality and performance of the optical signal of the high-speed optical module, as well as the degree of matching with the receiving end. When testing the optical characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as PAM4 for 800Gbps or NRZ for 400Gbps, should be considered. When testing the optical characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the optical characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.
- Electrical characteristics: The electrical characteristics mainly include parameters such as voltage, current, power consumption, jitter, and crosstalk, which reflect the quality and performance of the electrical signals of the high-speed optical module, as well as the degree of matching with the host board. When testing the electrical characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, humidity, voltages, fiber lengths, fiber types, fiber connectors and other factors should be considered, as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as 800Gbps PAM4 or 400Gbps NRZ. When testing the electrical characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the electrical characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.
- Functional characteristics: Functional characteristics mainly include the programming and control functions of the high-speed optical module, such as I2C, MDIO, CMIS, etc., which reflect the configurability and manageability of the high-speed optical module, as well as the communication capability with the host board. When testing the functional characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as PAM4 at 800 Gbps or NRZ at 400 Gbps, should be considered. When testing the functional characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the functional characteristics of the high-speed optical module meets the specifications and requirements.

- Compatibility features: Compatibility features mainly include the compatibility of high-speed optical modules with different host boards, switches, routers and other equipment, as well as with different protocols and standards, such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, InfiniBand and so on. When testing the compatibility characteristics, the effects of different temperatures, voltages, fibre lengths, fibre types, fibre connectors, etc., as well as the requirements of different data rates and modulation formats, such as 800Gbps PAM4 or 400Gbps NRZ, etc., should be considered. When testing the compatibility characteristics, reference should be made to relevant technical standards, such as [IEEE 802.3bs], [IEEE 802.3ck], [OIF CEI-56G], etc., as well as different application scenarios, such as data centre, cloud computing, 5G, etc., to assess whether the compatibility characteristics of the high-speed optical modules satisfy the specifications and requirements.
- Test results: Test results should be presented in a clear and objective manner, including data, charts, analyses, evaluations, etc., as well as comparisons and assessments with relevant technical standards and application requirements. The test results should be able to reflect the advantages and shortcomings of high-speed optical modules, as well as possible problems and suggestions for improvement.
800G/400G high-speed optical modules need to use what test equipment?
- BER instrument: Used to test the optical module's BER, eye diagram, clock recovery, forward error correction and other parameters, such as the 8-channel 400G PAM4 BER instrument from Unicom Instruments.
- Sampling Oscilloscope: Used to test the optical signal waveform, amplitude, phase, frequency and other parameters of the optical module, such as EXFO's EA-4000 Eye Analyzer.
- Optical Power Meter: Used to test the optical power, spectrum, wavelength and other parameters of optical modules, such as EXFO's FTBx-9160 NEMS optical switch.
- Optical Attenuator: Used to test the sensitivity, dynamic range, signal-to-noise ratio and other parameters of optical modules, such as EXFO's MXS-9100 MEMS Matrix Optical Switch.
- Optical Module Test Board (MCB): Used to connect optical modules and test equipment for serial communication and control, such as EXFO's Module Compliance Boardhtt








