Optical vs. all-optical networks, do you know what the difference is?
Today we're going to talk about a very interesting topic, which is optical networks and all-optical networks. What is an optical network, you may ask? What is an all-optical network? What's the difference between them? And what do they mean?
We should know that optical network is a network technology that uses optical signals to transmit information, and it is one of the important infrastructures of modern information society. With the development of Internet technology, human demand for network bandwidth continues to grow rapidly and explosively, optical network technology is also facing the challenge of improving transmission rate, capacity and quality. So what are the advantages of optical networks? Simply put, it is fast, big and good.
Fast: Optical signals are a kind of electromagnetic waves, and their propagation speed is close to the speed of light in a vacuum, which is much higher than that of electrical signals. Therefore, optical networks can achieve high-speed information transmission.
Large: optical signals have a high frequency and a wide frequency band, so they can carry a lot of information. Therefore, optical networks can realise large-capacity information transmission.
Good: Optical signal has strong anti-interference ability and low loss rate, so it can ensure the stability and quality of information transmission. Therefore, optical networks can achieve high-quality information transmission.
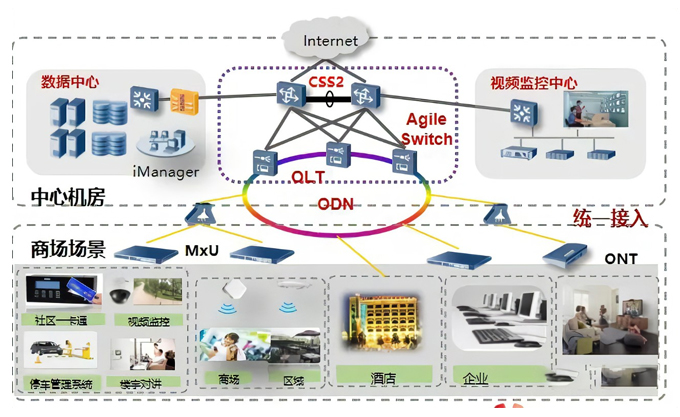
Due to these advantages, optical networks have been widely used in various fields, such as telecommunications, Internet, broadcasting and television, data centres, cloud computing, etc. However, optical networks also have some challenges and limitations. So, what are the challenges of optical networks? Simply put, it is difficult, expensive, and hard.
Difficult: Optical signal is a non-linear fluctuation phenomenon, and its transmission process is affected by various physical effects and environmental factors. Therefore, optical networks require complex theoretical models and algorithms to analyse and control.
Expensive: Optical signals require special devices and materials to generate, modulate, detect and process. Therefore, optical networks require expensive equipment and resources to build and maintain.
Difficult: Optical and electrical signals need to be interconverted. Therefore, optical networks require complex interfaces and protocols to interoperate and interconnect.
Due to these challenges and limitations, optical networks have yet to fully realise their potential performance and efficiency. So, is there a better solution? The answer is yes, and that is an all-optical network.
What is All-Optical Network?
All-Optical Network (All-Optical Network) is a network technology that uses only optical signals for information transmission, switching, routing and processing in the entire network. It is a revolutionary improvement over traditional hybrid electrical/optical networks. It can eliminate the bottleneck of electrical/optical conversion, improve the speed, capacity and quality of the network, and reduce the cost and power consumption of the network. So what are the characteristics of an all-optical network? Simply put, it is all, new and strong.
All: All-optical network realises the transmission of optical signals from end to end without any electrical/optical conversion. Therefore, all-optical network can avoid the delay, loss and interference of electric/optical conversion, and improve the efficiency and reliability of the network.
New: All-optical network adopts new types of optical devices and optical technologies, such as tunable lasers, wavelength division multiplexing, optical switching, optical routing and optical processing. As a result, all-optical networks enable more flexible network configuration and management, and richer network functions and services.
Strong: All-optical network makes use of the nonlinear characteristics and multi-wavelength characteristics of optical signals, such as self-phase modulation, cross-phase modulation, four-wave mixing, Raman scattering and so on. As a result, all-optical networks can achieve higher network performance and capacity, greater network adaptability and intelligence.
Due to these features, all-optical networks are considered to be the development direction and goal of future networks. However, all-optical networks also still face some technical difficulties and challenges. So, what are the difficulties of all-optical networks? Simply put, it is less, harder and farther away.
Less: All-optical network still lacks mature technical standards and specifications, perfect testing and evaluation methods, and extensive application and verification cases. Therefore, all-optical network still needs more research and development investment, more industrial and market support.
Difficulty: All-optical networks still have some technical difficulties and bottlenecks, such as the stability and reliability of tunable lasers, the dispersion and crosstalk problems of wavelength division multiplexing, the control and scheduling problems of optical switching and routing, and the algorithms and implementation problems of optical processing. Therefore, the all-optical network still needs more innovative and breakthrough solutions, more cooperation and communication platforms.
Far: All-optical network has not yet reached the level and scale of commercialisation, has not yet formed a complete industrial chain and ecosystem, and has not yet been popularised to a wide range of user groups. Therefore, the all-optical network still needs more time and opportunities to promote its development and application, and more publicity and education to improve its recognition and influence.
In conclusion, all-optical network is a network technology with great potential and prospect, which is a kind of optimisation and upgrading of the traditional hybrid electric/optical network. It can bring faster, bigger and better information transmission services to human society. However, it also has many problems and challenges that need to be solved. We expect it to become a reality soon and create a better future for us!
Today we're going to talk about a very interesting topic, which is optical networks and all-optical networks. What is an optical network, you may ask? What is an all-optical network? What's the difference between them? And what do they mean?
We should know that optical network is a network technology that uses optical signals to transmit information, and it is one of the important infrastructures of modern information society. With the development of Internet technology, human demand for network bandwidth continues to grow rapidly and explosively, optical network technology is also facing the challenge of improving transmission rate, capacity and quality. So what are the advantages of optical networks? Simply put, it is fast, big and good.
Fast: Optical signals are a kind of electromagnetic waves, and their propagation speed is close to the speed of light in a vacuum, which is much higher than that of electrical signals. Therefore, optical networks can achieve high-speed information transmission.
Large: optical signals have a high frequency and a wide frequency band, so they can carry a lot of information. Therefore, optical networks can realise large-capacity information transmission.
Good: Optical signal has strong anti-interference ability and low loss rate, so it can ensure the stability and quality of information transmission. Therefore, optical networks can achieve high-quality information transmission.

Due to these advantages, optical networks have been widely used in various fields, such as telecommunications, Internet, broadcasting and television, data centres, cloud computing, etc. However, optical networks also have some challenges and limitations. So, what are the challenges of optical networks? Simply put, it is difficult, expensive, and hard.
Difficult: Optical signal is a non-linear fluctuation phenomenon, and its transmission process is affected by various physical effects and environmental factors. Therefore, optical networks require complex theoretical models and algorithms to analyse and control.
Expensive: Optical signals require special devices and materials to generate, modulate, detect and process. Therefore, optical networks require expensive equipment and resources to build and maintain.
Difficult: Optical and electrical signals need to be interconverted. Therefore, optical networks require complex interfaces and protocols to interoperate and interconnect.
Due to these challenges and limitations, optical networks have yet to fully realise their potential performance and efficiency. So, is there a better solution? The answer is yes, and that is an all-optical network.
What is All-Optical Network?
All-Optical Network (All-Optical Network) is a network technology that uses only optical signals for information transmission, switching, routing and processing in the entire network. It is a revolutionary improvement over traditional hybrid electrical/optical networks. It can eliminate the bottleneck of electrical/optical conversion, improve the speed, capacity and quality of the network, and reduce the cost and power consumption of the network. So what are the characteristics of an all-optical network? Simply put, it is all, new and strong.
All: All-optical network realises the transmission of optical signals from end to end without any electrical/optical conversion. Therefore, all-optical network can avoid the delay, loss and interference of electric/optical conversion, and improve the efficiency and reliability of the network.
New: All-optical network adopts new types of optical devices and optical technologies, such as tunable lasers, wavelength division multiplexing, optical switching, optical routing and optical processing. As a result, all-optical networks enable more flexible network configuration and management, and richer network functions and services.
Strong: All-optical network makes use of the nonlinear characteristics and multi-wavelength characteristics of optical signals, such as self-phase modulation, cross-phase modulation, four-wave mixing, Raman scattering and so on. As a result, all-optical networks can achieve higher network performance and capacity, greater network adaptability and intelligence.
Due to these features, all-optical networks are considered to be the development direction and goal of future networks. However, all-optical networks also still face some technical difficulties and challenges. So, what are the difficulties of all-optical networks? Simply put, it is less, harder and farther away.
Less: All-optical network still lacks mature technical standards and specifications, perfect testing and evaluation methods, and extensive application and verification cases. Therefore, all-optical network still needs more research and development investment, more industrial and market support.
Difficulty: All-optical networks still have some technical difficulties and bottlenecks, such as the stability and reliability of tunable lasers, the dispersion and crosstalk problems of wavelength division multiplexing, the control and scheduling problems of optical switching and routing, and the algorithms and implementation problems of optical processing. Therefore, the all-optical network still needs more innovative and breakthrough solutions, more cooperation and communication platforms.
Far: All-optical network has not yet reached the level and scale of commercialisation, has not yet formed a complete industrial chain and ecosystem, and has not yet been popularised to a wide range of user groups. Therefore, the all-optical network still needs more time and opportunities to promote its development and application, and more publicity and education to improve its recognition and influence.
In conclusion, all-optical network is a network technology with great potential and prospect, which is a kind of optimisation and upgrading of the traditional hybrid electric/optical network. It can bring faster, bigger and better information transmission services to human society. However, it also has many problems and challenges that need to be solved. We expect it to become a reality soon and create a better future for us!







