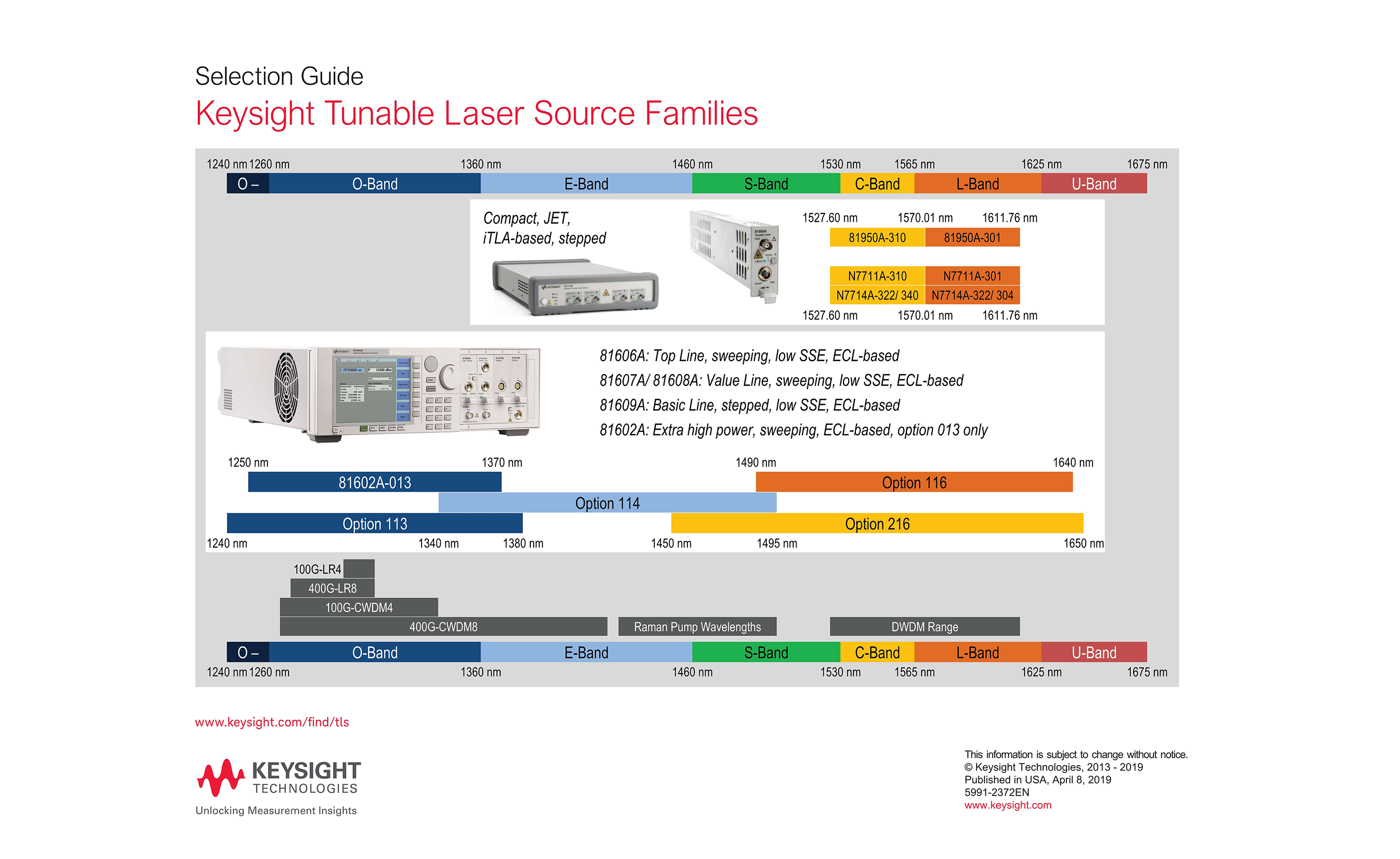
How to choose the right Tunable laser source
- Tuning range: Different applications may require different wavelength ranges, for example, near to mid-infrared tunable lasers can be used in areas such as gas sensing, environmental monitoring and chemical analysis. The wider the tuning range, the wider the application of the tunable laser.
- Tuning speed: Tuning speed refers to the rate at which the laser changes wavelength, usually expressed in nm/s or GHz/s. The faster the tuning speed, the faster the tunable laser can scan different wavelengths, improving measurement efficiency and resolution.
- Output Power: Output power refers to the intensity of light output from the laser, usually expressed in mW or dBm. The higher the output power, the stronger the signal the tunable laser can provide, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio and sensitivity, and can also be used for high-power applications such as materials processing and optical communications.
- Linewidth: Linewidth refers to the frequency width of the light output from the laser, usually expressed in MHz or pm. The narrower the linewidth, the purer the light can be provided by the tunable laser, reducing wavelength drift and mode hopping, and can also be used for high-resolution spectroscopy and optical information processing, etc.
- Stability: Stability refers to the degree of stability of the wavelength and power of the light output from the laser, usually expressed in pm or %. The higher the stability, the more reliable light the tunable laser can provide, reducing measurement errors and noise, and also can be used for long-time continuous measurement and control, etc.
- Tuning range: Different applications may require different wavelength ranges, for example, near to mid-infrared tunable lasers can be used in areas such as gas sensing, environmental monitoring and chemical analysis. The wider the tuning range, the wider the application of the tunable laser.
- Tuning speed: Tuning speed refers to the rate at which the laser changes wavelength, usually expressed in nm/s or GHz/s. The faster the tuning speed, the faster the tunable laser can scan different wavelengths, improving measurement efficiency and resolution.
- Output Power: Output power refers to the intensity of light output from the laser, usually expressed in mW or dBm. The higher the output power, the stronger the signal the tunable laser can provide, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio and sensitivity, and can also be used for high-power applications such as materials processing and optical communications.
- Linewidth: Linewidth refers to the frequency width of the light output from the laser, usually expressed in MHz or pm. The narrower the linewidth, the purer the light can be provided by the tunable laser, reducing wavelength drift and mode hopping, and can also be used for high-resolution spectroscopy and optical information processing, etc.
- Stability: Stability refers to the degree of stability of the wavelength and power of the light output from the laser, usually expressed in pm or %. The higher the stability, the more reliable light the tunable laser can provide, reducing measurement errors and noise, and also can be used for long-time continuous measurement and control, etc.








