If you work on electronic circuits, then you need to use an oscilloscope!
But what is the easiest oscilloscope to use?
An oscilloscope is a device used to test electronic circuits, allowing you to see how voltages change over time in order to diagnose problems in digital waveforms. It can record changes or variations in voltage over a period of time.
Learning how to use an oscilloscope is an essential step for electrical engineers. The ability to use this device is necessary for circuit analysis. Without this tool, it is almost impossible to find faults in complex circuits.
Let's learn more about oscilloscopes with the help of this article.
Digital storage oscilloscopes and cathode ray oscilloscopes.
An oscilloscope used for digital storage and analysis rather than analog technology is a digital storage oscilloscope.
It is a complex electronic device that consists of various electronic hardware software and modules. They are known to work in unison to capture, process, store and display data representing the signals of interest owned by the operator.
Also known as digital oscilloscope or digital sampling oscilloscope, it is the most commonly used oscilloscope. It is used for various purposes such as measurement functions, storage, display and advanced triggers that it is known for providing to its users.
The input analog signal is sampled and further converted into digital records. These digital records are found to be the amplitude of the signal during each sample time.
There are many subtypes of digital storage oscilloscopes that came into use after the introduction of digital technology.
Usually, all these types are referred to by the term digital oscilloscope itself. Other terms are used only when they are to be specifically mentioned.
Usually, it is referred to as digital oscilloscope and digital fluorescent oscilloscope or DPO. digital storage oscilloscope - this term came into existence after the introduction of digital oscilloscopes.
The name indicates that it has memory that can be used for storage. These stores may be waveforms that are visible for long periods of time.
Digital storage oscilloscopes are known for storing and digitizing input signals.
It is convenient and can be used in a variety of applications and industries to accomplish multiple tasks.
图片来源:卓越物理
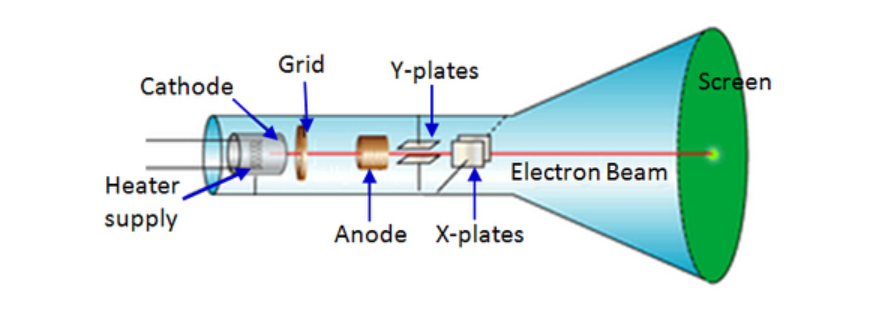
In the early days, oscilloscopes consisted of cathode ray tubes (CRTs). This is why they were called cathode ray oscilloscopes.
Basics of O-scopes.
An O-scope is used to plot electrical signals over time, as you know most oscilloscopes produce two types of dimensional plots.
It generates a graph waiting time on the x-axis and another graph waiting time with voltage on the y-axis. Different types of controls are provided on the oscilloscope screen.
With the help of these controls, the graph can be scaled vertically and horizontally. These controls allow to zoom in and out of the signal. With the help of the controls, you can set the triggers for the fractions to help focus and stabilize the discipline.
History of oscilloscopes:

Andre Blondel was a French physicist who invented the oscilloscope in 1893.
He built and demonstrated the first electro-mechanical oscilloscope, a device that recorded the electrical values in it.
It recorded the electrical power of the current, such as the current genetic strength. With the help of an ink pendulum connected to a coil, the information was recorded on a moving paper tape.
The bandwidth of these mechanical devices ranged from 10 to 19 kHz. Oscilloscope became a universal measuring tool in 1957, and the production of this device began in all technologically advanced countries.
The device can be divided into two categories: analog and digital, which have their positive and negative sides and have their own unique features.
Digital storage oscilloscope working principle.
Digital storage oscilloscopes are used to store and digitize input signals. This is done by using a cathode ray tube or CRT and with the help of a digital memory. Digitization is usually accomplished by sampling the input signal using various periodic waveforms.
Nowadays, measuring the maximum frequency of a signal with the help of a DSO depends mainly on two factors. These factors are the sampling rate and the nature of the converter. In the sampling rate, the safe analysis of the input signal is done using the sampling theory.
This theory states that it is crucial that the sampling rate of the signal is twice the highest frequency of the received input signal. Sampling rate refers to the fact that the analog-to-digital conversion rate is fast and high.
In the work of digital storage oscilloscopes, converters work with expensive flash memory whose resolution decreases as the sampling rate increases. The bandwidth and resolution of the oscilloscope is limited due to the sample rate.
The need for an analog-to-digital signal converter can be easily overcome by using shift registers. Shift registers are used to sample and store the input signal. The signal is read out slowly and stored in digital form from the shift register.
When this approach is followed, it is noted that the cost of the converter is greatly reduced. It is known for operating up to 100 giant samples per second.The DSO does not accept data input during digitization, which is a disadvantage of digital storage oscilloscopes.
To visualize the final wave, the oscilloscope is known for its use of interpolarization techniques. This technique is the process of creating new data points by using variable data points. These points are connected together with the help of two processes: linear interpolation and sinusoidal interpolation.
These lines are used to connect the points together during interpolation. It is used to create square waves or pulses. In the case of sine waveform, sine interpolation is used in DSO.
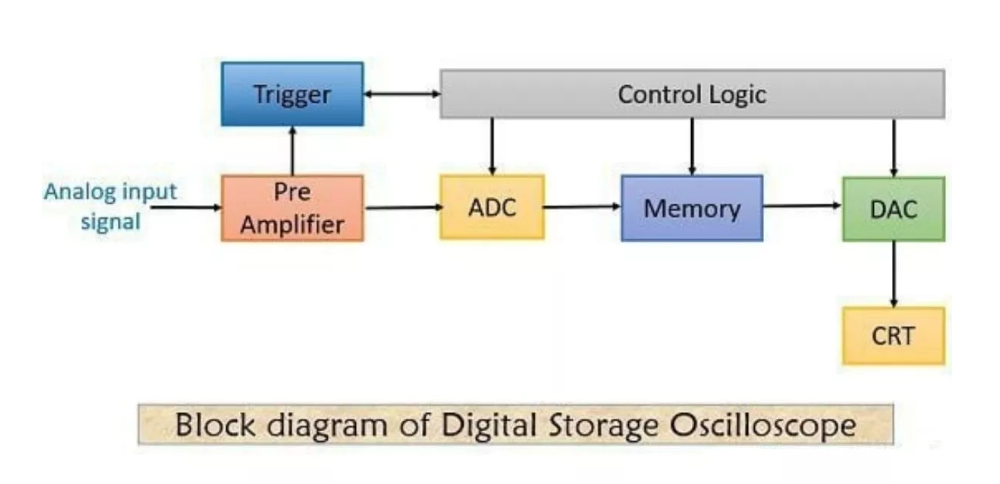
A digital oscilloscope includes a digitizer, amplifier, analyzer circuit, memory, waveform reconstruction, horizontal board, vertical board, cathode ray tube or CRT, flip-flop, clock, time base circuit, clock and horizontal amplifier.
The DSO digitizes the analog input signals and amplifies these signals if they are found to be weak. Once amplification occurs, the signals are digitized and further stored in memory. Once the waveform is reconstructed, these digital signals are processed by the analyzer circuitry.
*** Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version) ***
If you work on electronic circuits, then you need to use an oscilloscope!
But what is the easiest oscilloscope to use?
An oscilloscope is a device used to test electronic circuits, allowing you to see how voltages change over time in order to diagnose problems in digital waveforms. It can record changes or variations in voltage over a period of time.
Learning how to use an oscilloscope is an essential step for electrical engineers. The ability to use this device is necessary for circuit analysis. Without this tool, it is almost impossible to find faults in complex circuits.
Let's learn more about oscilloscopes with the help of this article.
Digital storage oscilloscopes and cathode ray oscilloscopes.
An oscilloscope used for digital storage and analysis rather than analog technology is a digital storage oscilloscope.
It is a complex electronic device that consists of various electronic hardware software and modules. They are known to work in unison to capture, process, store and display data representing the signals of interest owned by the operator.
Also known as digital oscilloscope or digital sampling oscilloscope, it is the most commonly used oscilloscope. It is used for various purposes such as measurement functions, storage, display and advanced triggers that it is known for providing to its users.
The input analog signal is sampled and further converted into digital records. These digital records are found to be the amplitude of the signal during each sample time.
There are many subtypes of digital storage oscilloscopes that came into use after the introduction of digital technology.
Usually, all these types are referred to by the term digital oscilloscope itself. Other terms are used only when they are to be specifically mentioned.
Usually, it is referred to as digital oscilloscope and digital fluorescent oscilloscope or DPO. digital storage oscilloscope - this term came into existence after the introduction of digital oscilloscopes.
The name indicates that it has memory that can be used for storage. These stores may be waveforms that are visible for long periods of time.
Digital storage oscilloscopes are known for storing and digitizing input signals.
It is convenient and can be used in a variety of applications and industries to accomplish multiple tasks.

图片来源:卓越物理
In the early days, oscilloscopes consisted of cathode ray tubes (CRTs). This is why they were called cathode ray oscilloscopes.
Basics of O-scopes.
An O-scope is used to plot electrical signals over time, as you know most oscilloscopes produce two types of dimensional plots.
It generates a graph waiting time on the x-axis and another graph waiting time with voltage on the y-axis. Different types of controls are provided on the oscilloscope screen.
With the help of these controls, the graph can be scaled vertically and horizontally. These controls allow to zoom in and out of the signal. With the help of the controls, you can set the triggers for the fractions to help focus and stabilize the discipline.
History of oscilloscopes:

Andre Blondel was a French physicist who invented the oscilloscope in 1893.
He built and demonstrated the first electro-mechanical oscilloscope, a device that recorded the electrical values in it.
It recorded the electrical power of the current, such as the current genetic strength. With the help of an ink pendulum connected to a coil, the information was recorded on a moving paper tape.
The bandwidth of these mechanical devices ranged from 10 to 19 kHz. Oscilloscope became a universal measuring tool in 1957, and the production of this device began in all technologically advanced countries.
The device can be divided into two categories: analog and digital, which have their positive and negative sides and have their own unique features.
Digital storage oscilloscope working principle.
Digital storage oscilloscopes are used to store and digitize input signals. This is done by using a cathode ray tube or CRT and with the help of a digital memory. Digitization is usually accomplished by sampling the input signal using various periodic waveforms.

Nowadays, measuring the maximum frequency of a signal with the help of a DSO depends mainly on two factors. These factors are the sampling rate and the nature of the converter. In the sampling rate, the safe analysis of the input signal is done using the sampling theory.
This theory states that it is crucial that the sampling rate of the signal is twice the highest frequency of the received input signal. Sampling rate refers to the fact that the analog-to-digital conversion rate is fast and high.
In the work of digital storage oscilloscopes, converters work with expensive flash memory whose resolution decreases as the sampling rate increases. The bandwidth and resolution of the oscilloscope is limited due to the sample rate.
The need for an analog-to-digital signal converter can be easily overcome by using shift registers. Shift registers are used to sample and store the input signal. The signal is read out slowly and stored in digital form from the shift register.
When this approach is followed, it is noted that the cost of the converter is greatly reduced. It is known for operating up to 100 giant samples per second.The DSO does not accept data input during digitization, which is a disadvantage of digital storage oscilloscopes.
To visualize the final wave, the oscilloscope is known for its use of interpolarization techniques. This technique is the process of creating new data points by using variable data points. These points are connected together with the help of two processes: linear interpolation and sinusoidal interpolation.
These lines are used to connect the points together during interpolation. It is used to create square waves or pulses. In the case of sine waveform, sine interpolation is used in DSO.
A digital oscilloscope includes a digitizer, amplifier, analyzer circuit, memory, waveform reconstruction, horizontal board, vertical board, cathode ray tube or CRT, flip-flop, clock, time base circuit, clock and horizontal amplifier.
The DSO digitizes the analog input signals and amplifies these signals if they are found to be weak. Once amplification occurs, the signals are digitized and further stored in memory. Once the waveform is reconstructed, these digital signals are processed by the analyzer circuitry.
*** Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version) ***







